Structure, Phrasing and Display
Structural (block) elements stack vertically on top of each other in new lines. Block elements are subject to the effects of positioning properties. To make a block element behave like an inline element, you can use Display: Inline in CSS.
Phrasing (inline) elements stay within the horizontal sequence that surrounds them, such as a sequence of text. To make an inline element behave like a block, you can use Display: Block in CSS.
| Display Property |
Use on Block? |
Use on Inline? |
Description |
| Block |
N |
Y |
Makes an inline element behave like a block and appear on a new line. |
| Inline |
Y |
N |
Makes a block element remain inline instead of starting on a new line. |
| Inline-Block |
Y |
Y |
Combines features of both. The element will appear on the same line, but you can set the width, height, margin-top, and margin-bottom as if it were a block. |
| Flex |
Y |
N |
Arranges child block elements in a Flex container. Each child becomes a Flex Item. Their default arrangement is in a horizontal row, ordered from left to right. |
| Grid |
Y |
N |
Arranges child block elements into a grid container with rows and columns. Each child becomes a Grid Item. By default, the grid has one column so the elements will remain stacked vertically until the rows and columns are defined. |
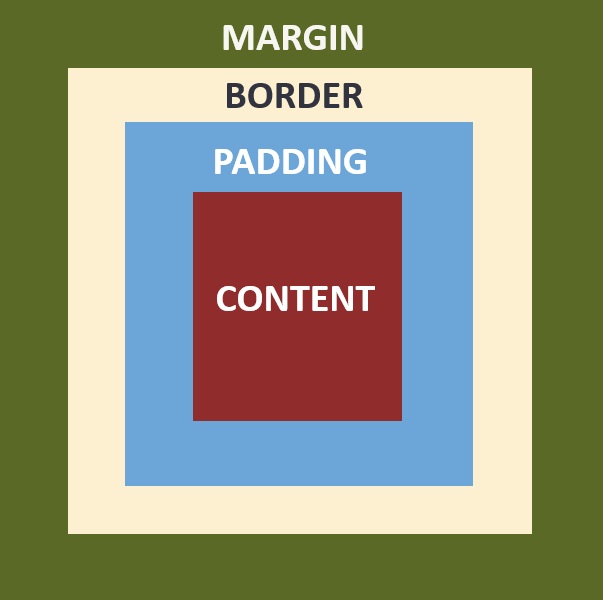
Box Model
Every HTML element is contained in a box that is made up of four parts: content, padding, borders, and margins. You can use CSS properties to determine the width of each part, which affects how the element will lay on the webpage in relation to the elements around it. The border can also be given a color and style.
The total width and height of an element can be styled using the box-sizing property. The default value, content-box, applies width and height properties to only the content area of an element. This can make it difficult to calculate the total size of an element because you must add the width of each part.
The border-box value, which is often the preferred value, applies width and height to the content, padding, and border, making it easier to know the total size of the visible element.
Background Images
This beautiful background image is displayed using the CSS Background-Image property! Background images are decorative. They are often used to add texture or differentiate space, such as a banner. They are not accessible by screen readers and do not affect the page's SEO.
To add an image that contributes to the content of the page or communicates information, use the HTML Img element. Screen readers and SEO can access the Alt attribute and read the image's description. Images in HTML can also be used for interactive elements on the webpage.
